The techniques, equipment, and materials employed in creating and manufacturing furniture are the primary differences between modern and traditional furniture approaches. Here are some significant differences:
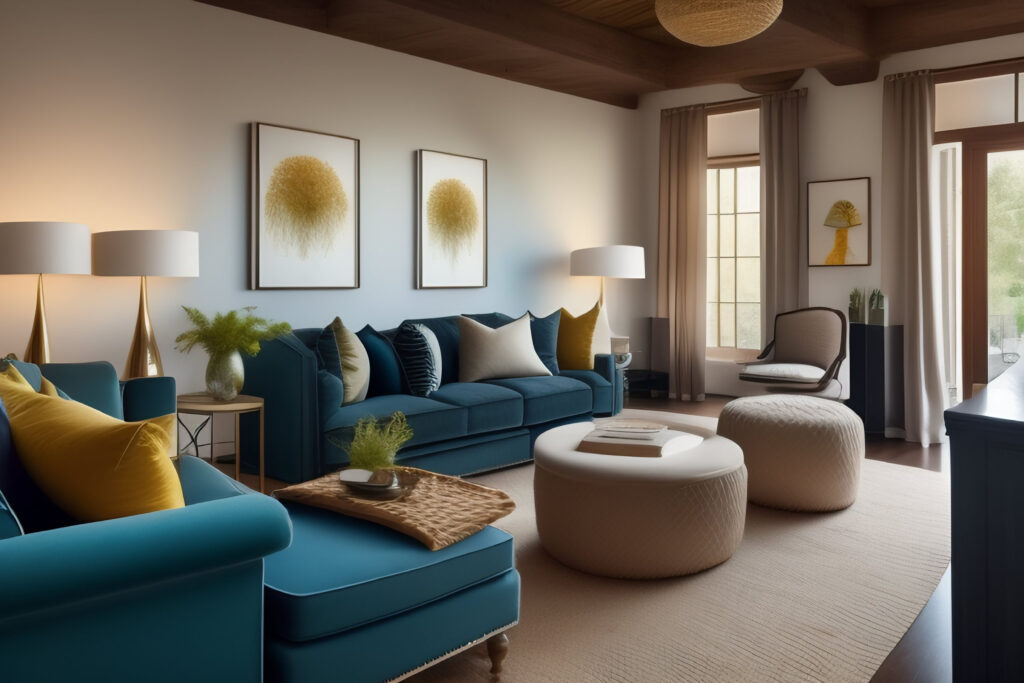

Traditional Furniture Techniques:
- Handcraftsmanship: Traditional furniture is typically crafted by skilled artisans who use hand tools and techniques passed down through generations. Handcraftsmanship is highly valued, and each piece is often a unique work of art.
- Solid Wood Construction: Traditional furniture is often constructed from solid wood, such as oak, mahogany, cherry, or walnut. This solid wood is used for the frame, legs, and sometimes panels and veneers.
- Ornate Details: Traditional furniture features intricate carvings, elaborate moldings, and decorative inlays. These details are often done by hand and add to the piece’s aesthetic appeal.
- Dovetail Joints: Traditional furniture relies on time-tested joinery techniques like dovetail joints, mortise and tenon joints, and tongue and groove joints for strength and durability.
- Hand Finishing: The finishing process for traditional furniture involves hand-sanding, staining, and polishing to achieve a rich, deep luster. Patience and skill are required for this part of the process.
- Upholstery: Upholstered traditional furniture may use natural materials like horsehair, cotton, or down for cushioning, and the upholstery is often tufted or stitched by hand.
- Limited Mass Production: Traditional furniture is typically produced in smaller quantities, with an emphasis on quality over quantity. Each piece is often custom-made or made in small batches.
Modern Furniture Techniques:
- Industrial Manufacturing: Modern furniture is often mass-produced using industrial manufacturing processes. This includes the use of computer-controlled machinery and assembly line production.
- Engineered Materials: Contemporary furniture frequently incorporates engineered materials like plywood, MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard), and particleboard in addition to solid wood. These materials are chosen for their cost-effectiveness and durability.
- Simplicity in Design: Modern furniture is known for its clean lines, minimalist designs, and a focus on function over ornamentation. It often features sleek and unadorned surfaces.
- Screwed and Glued Joints: While some modern furniture still uses traditional joinery methods, many pieces rely on screws, dowels, and adhesives for assembly, which can be faster and more cost-effective.
- Sprayed Finishes: Finishing techniques for modern furniture often involve sprayed finishes, which are efficient and consistent but may lack the handcrafted charm of traditional finishes.
- Mass Production: Modern furniture is typically produced in larger quantities, leading to standardized designs and lower price points. This makes it more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Innovative Materials: Modern furniture frequently incorporates materials like metal, glass, plastic, and composite materials, allowing for a broader range of design possibilities and aesthetics.
- Eco-Friendly Practices: Many modern furniture manufacturers are increasingly focused on sustainability, using recycled materials and environmentally friendly production methods.
- Modularity: Some modern furniture is designed with modularity in mind, allowing for customizable configurations and easy assembly and disassembly.
It’s worth noting that contemporary furniture can vary widely in style and quality, and there is a growing trend of combining traditional craftsmanship with modern design sensibilities to create unique pieces that bridge the gap between these two approaches. Ultimately, the choice between traditional and modern furniture techniques depends on personal preferences, budget constraints, and the desired aesthetic for your living space.
 Cart is empty
Cart is empty